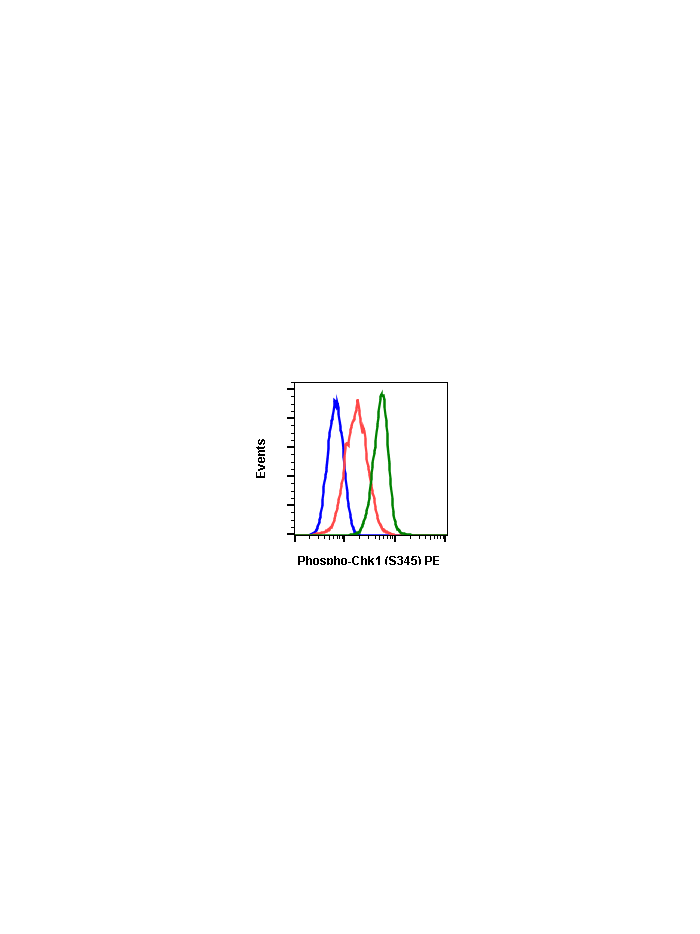
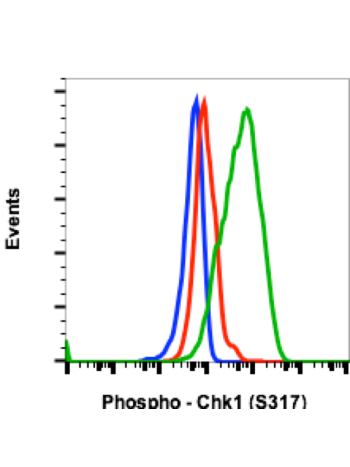
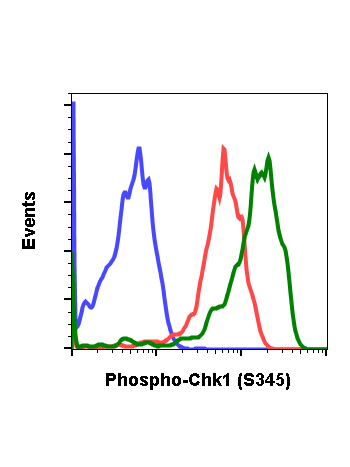
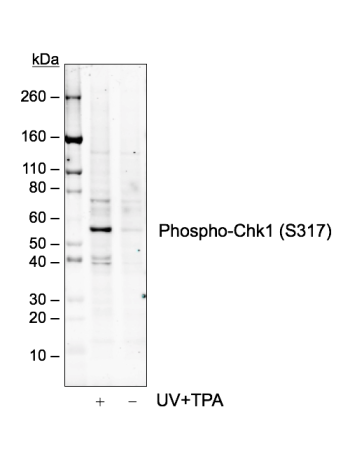
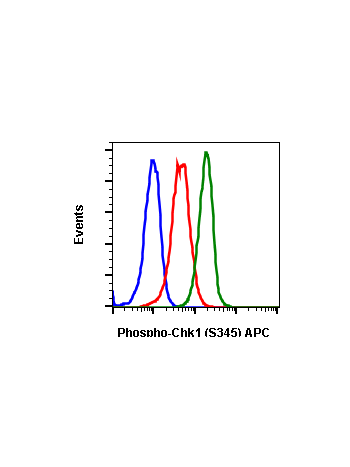
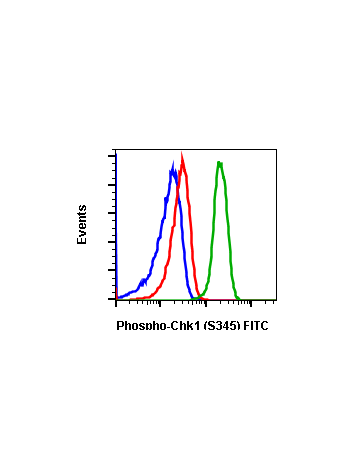
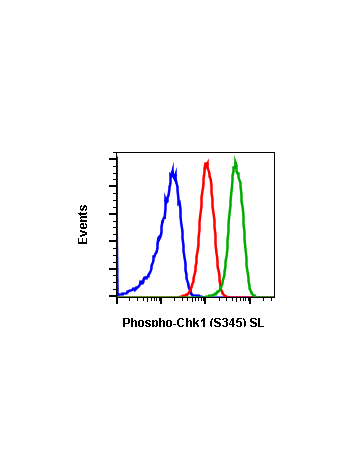
Phospho-Chk1 (Ser345) (R3F9) rabbit mAb PE conjugate
From
$118.80
In stock
Only %1 left
SKU
2192
The act of DNA damaged response and cell cycle checkpoints requires the activation of four protein kinases that form the canonical ATR-Chk1 and ATM-Chk2 pathways. ATR activation requires the generation of structures containing single strand DNA (ssDNA) adjacent to double strand DNA (dsDNA). Such ssDNA is coated with replication protein A complex and attracts ATR (1,2). The accumulation of ATR to damage sites results in initial activation of ATR. ATR phosphorylates proteins at the ssDNA which are called checkpoint regulators. The accumulation and phosphorylation of these checkpoint regulators further stimulates the catalytic activity of ATR. ATR-induced Chk1 phosphorylation likely occurs at the sites of DNA damage on chromatin (3-5). The activated ATR phosphorylates Ser317 and Ser345 of phospho Chk1 in its C-terminal regulatory domain. Phospho Chk1 is critical for DNA damage checkpoint activation, replication control, and cell viability (6-8). Functionally, ATR-mediated phosphorylation elevates Chk1 catalytic activity. The N-terminal catalytic domain of Chk1 adopts an open kinase conformation and the deletion of C-terminal domain increases Chk1 catalytic activity.
| Applications | Flow Cytometry |
|---|---|
| Clone | Chk1S345-R3F9 |
| Format | PE |
| Validated Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Cross Reactivity | Predicted to work with mouse, rat and other homologues. |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | A synthetic phospho-peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Ser345 of human phospho Chk1 |
| Formulation | 1X PBS, 0.09% NaN3, 0.2% BSA |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgGk |
| Preparation | Protein A+G |
| Recommended Usage | For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µL per million cells or 5 µL per 100 µL of staining volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application. |
| Storage | 2-8ºC |
| Pseudonyms | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1, CHK1 checkpoint homolog, Cell cycle checkpoint kinase, Checkpoint kinase-1, CHEK1 |
| Uniprot ID | O14757 |
| References | 1. Caprelli ML, et al. (2013) Cell Cycle, 12: 916-22. 2. Capasso H, et al. (2002) J. Cell Sci. 115: 4555-64. 3. Carrassa L, et al. (2011) Cell Cycle 10: 2121-8. 4. Chen MS, et al. (2003) Mol. Cell Biol. 23: 7488-97. 5. Ciccia A, et al. Mol. Cell 40: 179-204. 6. Cimprich CA, (2014) Oncogene 33: 3351-60 7. Cremona CA, et al. (2014) Oncogene 33: 3351-60. 8. Niida H, et al. (2007) Mol. Cell Biol. 27: 2572-81. |
Write Your Own Review